The GLACIER (GLAss Cutting and Removal) project: Glass cutting and thin optical glass layer removal with femtosecond lasers
Removing thin layers and cutting glass are the key steps for manufacturing products in strategic markets:
The cutting of multi-layer glass is currently limited by the thickness and:
- involves great difficulty (<300 µm) and complex shapes
- leaves edge defects that cause breakage in chemical reinforcement processes
Removal of top layers is limited by the necessity of preserving the optical quality of the substrate.
The “GLACIER” project offers a complete, versatile laser process designed on the basis of femtosecond laser beam shaping that enables:
Selective removal of thin layers on the glass substrate, thickness between 0.1 and 20 µm
- Cutting of treated glass, thickness up to 30 µm for all 2D shapes
- Quality control of the different steps: manipulation, cutting, quality of the substrate
- Optimization of the processes (speed, manipulation)
Industrial project innovation
The GLACIER solution offers several levels of innovation:
- Use of ultra-short sources that make it possible to sublimate and/or work the material in its mass by modifying the volume and preserving the quality of the surfaces
- The ability to machine a broad range of materials
- In-process monitoring and process automation for greater versatility and higher precision
- Versatility and reconfiguration – this makes it possible to perform multiple operations with the same laser machine (decoating)
HEF heads up this innovative project.
- Industrial mastery of thin-layer cutting and removal; mastery of the handling, cleaning, and packaging processes
- Development of a new surface treatment process.
- Selling the de-coating service + “shop-in-shop” machine proposition.
Contact
Valentin Maffeis
vmaffeis@hef.group

ECOCLIN project – Circular Economy and Energy Efficiency Applied to Nitriding Processes in Salt Baths – April 2021
The objectives of this project were to improve the environmental footprint of existing processes for nitriding in salt baths and modernize and digitalize the existing production lines and production units.
Various challenges were overcome to improve the competitiveness of CLINTM thanks to the ECOCLIN recycling projects, namely:
- Reducing waste
- Reducing the use of primary materials
- Reducing water use
- Reducing nitrogenous waste (global regulatory environment)
The primary objective of the ECOCLIN project is to develop an innovative procedure for recycling the effluents arising from nitriding in a molten salt bath in order to improve the environmental footprint of such recycling by promoting a circular economy approach.
Project milestones:
Setting up a full-scale demonstrator at our industrial site TECHNIQUES SURFACES ANDREZIEUX:
- Validating the process and the quality of the salts recovered from recycling
- Establishing regional recycling centers <>local recycling
- Reducing the carbon footprint
- Life cycle analysis
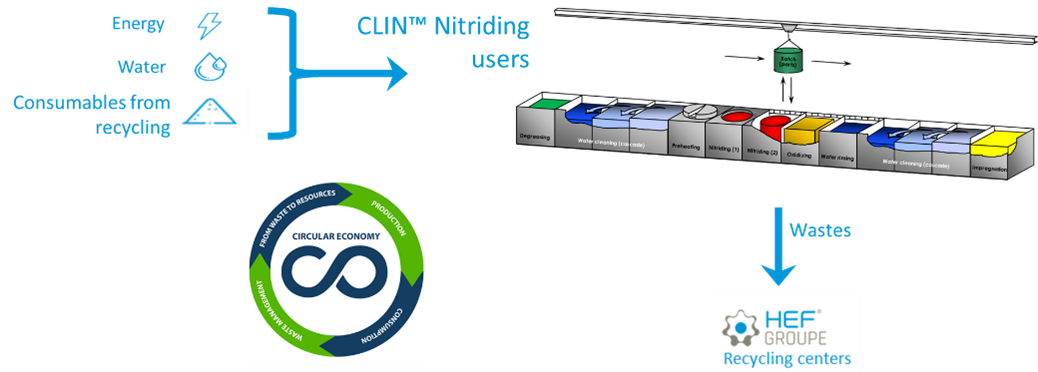
An innovative project, the ECO-CLIN process offers several levels of industrial innovation:
- Transformation of waste arising from the nitriding lines into a resource thanks to the ECOCLIN recycling process
- Reduction of water consumption
- Prevention of nitrogenous waste
- 5 patents filed / pending
HEF’s tasks in the project:
- Developing a new recycling process
- Deploying recycling centers in the major regions (Europe, India, China, the Americas)
- Designing and providing ECO-CLIN equipment
- Offering recycling services for licensees
Contact
Frédéric Garcia
fgarcia@hef.group

Development of interconnection balls for assembly with ball grid array (BGA) soldering
The SUPERBALL project was launched in October 2021 for an anticipated duration of 2 years with €800,000 funding. This award-winning project of the AAP R&D BOOSTER de la Région Auvergne Rhône-Alpes region is driven by IREIS (HEF’s central R&D organization), and also includes the Georges Friedel Laboratory at École des Mines de Saint-Étienne, and the companies Nicomatic and THALES AVS FRANCE SAS
The objectives of this project are to develop and industrialize a French manufacturing sector for high-performance (PCSB) interconnection balls for populating printed circuit boards with electronic components.
Polymer core solder balls are key products for:
- solder assembly by means of ball grid array (BGA) and ceramic ball grid array (CBGA) on printed circuit boards.
The SUPERBALL project targets the market for polymer-core solder balls, so that high-performance electronic equipment can function in harsh use conditions (significant temperature fluctuations, extreme mechanical conditions, corrosive atmospheres, etc.). For example, PCSB balls are used in the civil and military aerospace sector.
Polymer core solder balls improve the service life of the electrical contact for BGA assemblies on circuit boards.
Advantages:
- An alternative to conventional tin-alloy solder balls with or without lead
- Limit the thermomechanical stress on joints
- Eliminates use of underfill
- Improve reliability and reparability
- Compatible with reflow soldering as stipulated in the standard IPC-J-STD-001
- Miniaturization
- Flexible design with the possibility of different coatings / finishes
- Excellent corrosion resistance with extended service life (up to one year)
- Can be mounted with isotropically conductive adhesive (ICA) or a lead-free compatible solder paste
- Dimensional control (pitch & stand-off) of assemblies thanks to non-fusible solder balls
- Lead-free technology
- Weight savings
The SUPERBALL project offers several levels of industrial innovation:
- Increased assembly reliability through use of non-fusible, polymer-core solder balls that enable improved thermomechanical resistance of joints
- The ability to use different coatings on the solder balls
- A range of different diameters to address the needs of different markets
- Sending in a product for repair does not require use of an underfill, enabling reballing of BGA components
HEF’s tasks in the project:
Industrial control of functionalized powders. Development of a new product. Commercial development of the solder balls
Contact
Sébastien Bucher
sbucher@hef.group

Launching the TRIDEN project: Tribology for decarbonized energy (Nov 2023 to Oct 2026)
With the TRIDEN research and development project conducted by IREIS (the HEF Group’s research institute), the role played by surface materials and their properties in the mobility and energy production sectors has been reconsidered to facilitate the deployment of more eco-friendly energy. The project focuses on developing competencies as well as scientific and technical knowledge to improve sustainability and the efficacy of surface materials.
The targeted applications are hydrogen-based thermal engines (storage and distribution, injection components, combustion chambers) and the components of the cooling circuits for nuclear power plants (valves, etc.). This project is a response to new issues concerning the work environment of mechanical systems on the tribology map: pressure and a reducing or ionizing atmosphere, modification of lubricants or no lubrication at all, performance (or fragilization) of the materials (particularly in the presence of hydrogen). Co-financed by the French government as part of France 2030 and by the European Union – Next Generation EU as part of the France Relance plan, TRIDEN is one of the pioneers of these new standards of excellence and industrial project innovation in the field of tribology.
Contact:
Etienne Macron
emacron@hef.group
